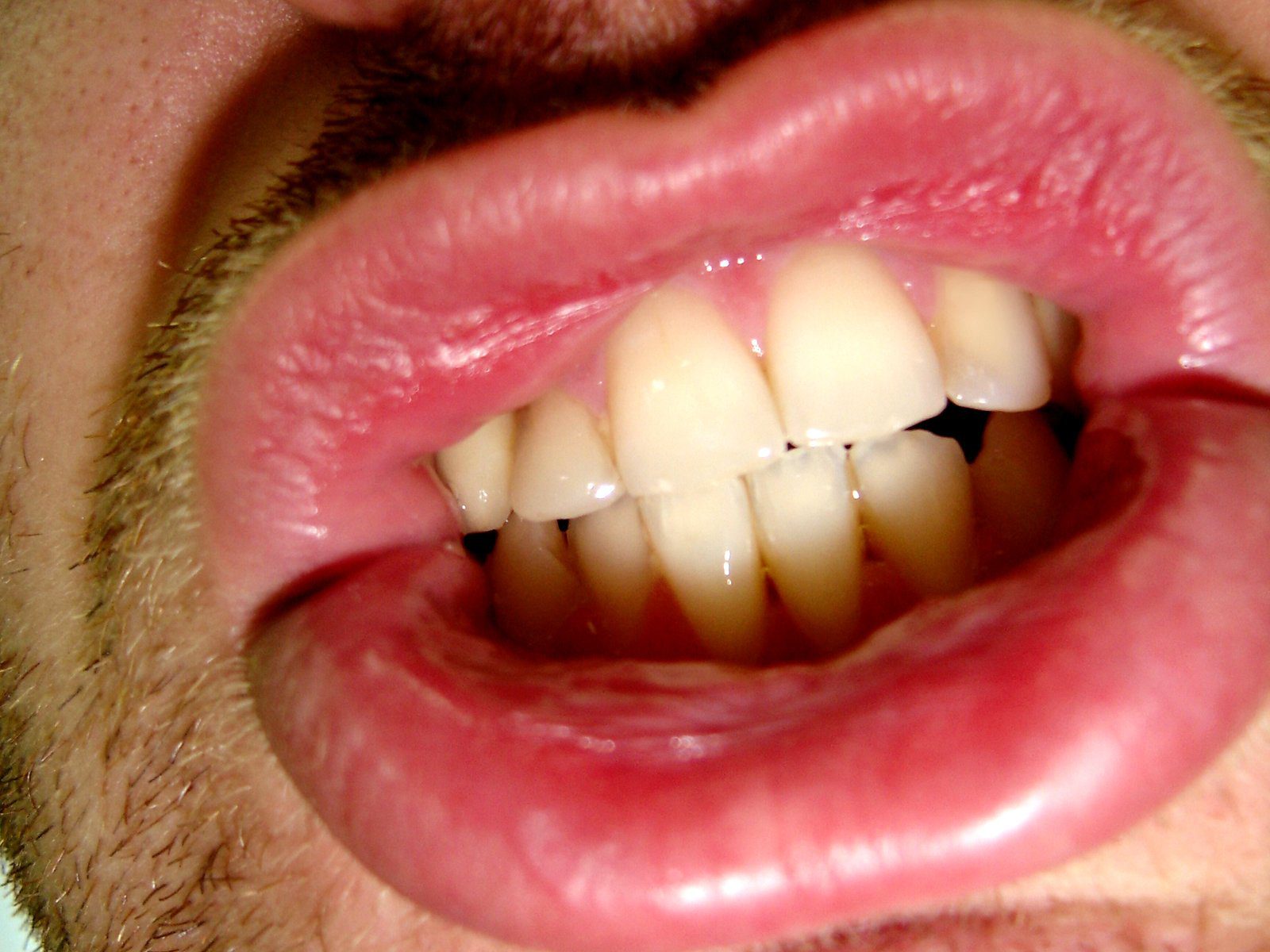
Gum disease is caused by bacteria that accumulate in the plaque that forms on the teeth. It leads to inflammation of the gums that can progress to affect the bone surrounding the teeth. If left unchecked, gum disease can cause teeth to become loose and eventually fall out.
(Freeimages / diego medrano)
There are three stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis – This is the earliest stage of gum disease. It is an inflammation of the gums caused by the build-up of plaque at the gumline. If not removed, the bacteria in the plaque produce toxins that will irritate the gum tissue, leading to gingivitis.
- Periodontitis – During this stage, the bone and fibers that anchor the teeth in place are damaged beyond repair. The gums will form a pocket below the gumline and trap food and plaque. Dental treatment and improved care of the teeth can prevent further damage.
- Advanced periodontitis – This is the final stage of gum disease, with the bone and fibers that support the teeth breaking down and causing the teeth to shift or loosen.
Gum disease may start out painlessly and go undetected. To catch gum disease in its earliest stages, watch for the following symptoms:
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums
- Red, swollen or tender gums
- Persistent bad breath and bad taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth
- Changes in the way your teeth come together
- Changes in the fitting of partial dentures
- Pus around the teeth and gums
- Teeth sensitivity to cold or hot temperatures
- Pain when chewing food
Prevention
To prevent gum disease, brush and floss daily. The use of antibacterial toothpaste or mouthwash can kill bacteria and reduce plaque in the mouth, which can, in turn, stave off gum disease.
Treatment
Dental plaque can be removed through professional cleanings. Make sure to see a dentist regularly to keep plaque at bay.
Your dentist can perform scaling and root planing if your disease is more advanced. An ultrasonic scaling device is used to remove plaque and tartar debris above and below the gum line. Laser treatments can also remove tartar deposits. In cases where the periodontal pockets are deeper than 5 mm, gingival flap surgery may be in order.
